- +1 (714) 578-6100
Hours Mon - Fri, 07:00 AM - 06:00 PM (Pacific Time)
Raw Materials
-
Posted: January 10, 2023Read more »
Terra customers often inquire about what type of steel is suggested for their product. In making a decision, one should also consider that not all 304 and 316 stainless steel is built to equal standards.
In the USA, the leading codes of standard practices for steel manufacturing are issued by the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC). The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system must be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification
-
Posted: January 03, 2023Read more »
Terra Universal manufactures a vast selection of stainless steel products for cleanrooms, hospitals, laboratories, and other controlled environments. Among these steel-constructed products, you'll find tables, workstations, glove boxes, pass-throughs, doors, and more.
-
Posted: March 01, 2019Read more »
This chart is intended as a general guide for various materials and chemicals. It shows some of the materials used in Terra’s products and chemicals likely to be used with them. Testing is strongly recommended for extreme conditions of use, such as prolonged exposure or immersion, high temperatures and high concentrations. The acids, caustics and salts in this chart are assumed to be in solution. Materials may react differently to the pure substances (glacial acetic acid, for example). See Terra Universal's line of plastic Desiccators.
Hazards Key
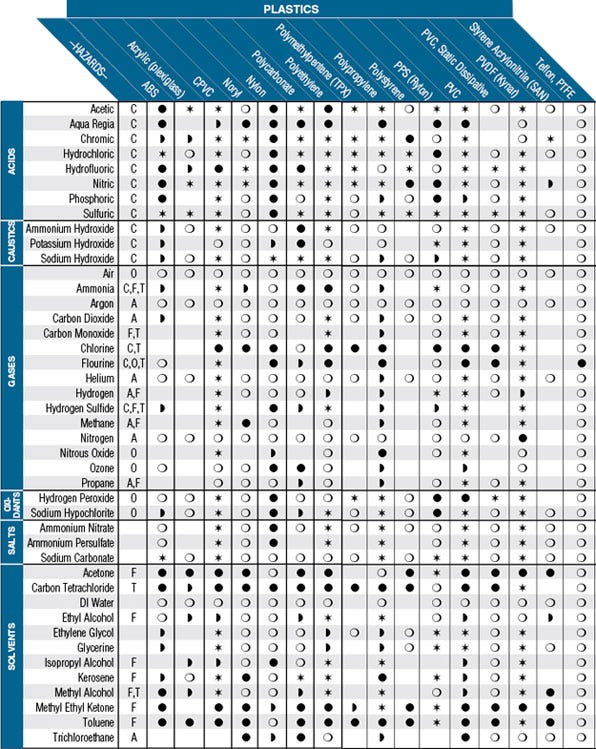
Hazards (Only the primary ones are shown. For example, chlorine is not shown as an asphyxiant because its toxicity will kill you first).
- A
-
Posted: February 28, 2019Read more »
This chart is intended as a general guide for various materials and chemicals. It shows some of the materials used in Terra’s products and chemicals likely to be used with them. Testing is strongly recommended for extreme conditions of use, such as prolonged exposure or immersion, high temperatures and high concentrations. The acids, caustics and salts in this chart are assumed to be in solution. Materials may react differently to the pure substances (glacial acetic acid, for example). See Terra Universal's line of Rubber & Synthetic Gloves.
Hazards Key
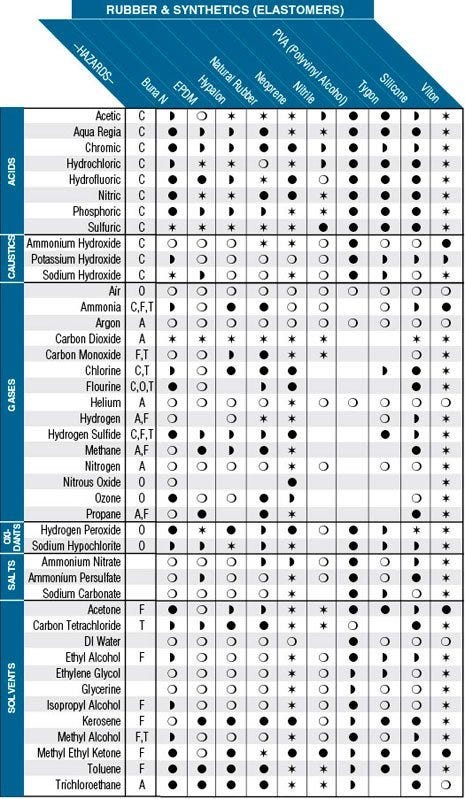
Hazards (Only the primary ones are shown. For example, chlorine is not shown as an asphyxiant because
-
Posted: February 15, 2019Read more »
This chart is intended as a general guide for various materials and chemicals. It shows some of the materials used in Terra’s products and chemicals likely to be used with them. Testing is strongly recommended for extreme conditions of use, such as prolonged exposure or immersion, high temperatures and high concentrations. The acids, caustics and salts in this chart are assumed to be in solution. Materials may react differently to the pure substances (glacial acetic acid, for example). See Terra Universal's line of metal Pass-Throughs.
Hazards Key
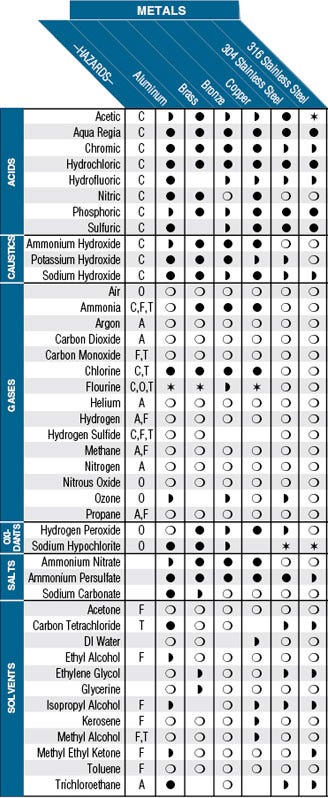
Hazards (Only the primary ones are shown. For example, chlorine is not shown as an asphyxiant because its toxicity will kill you first).